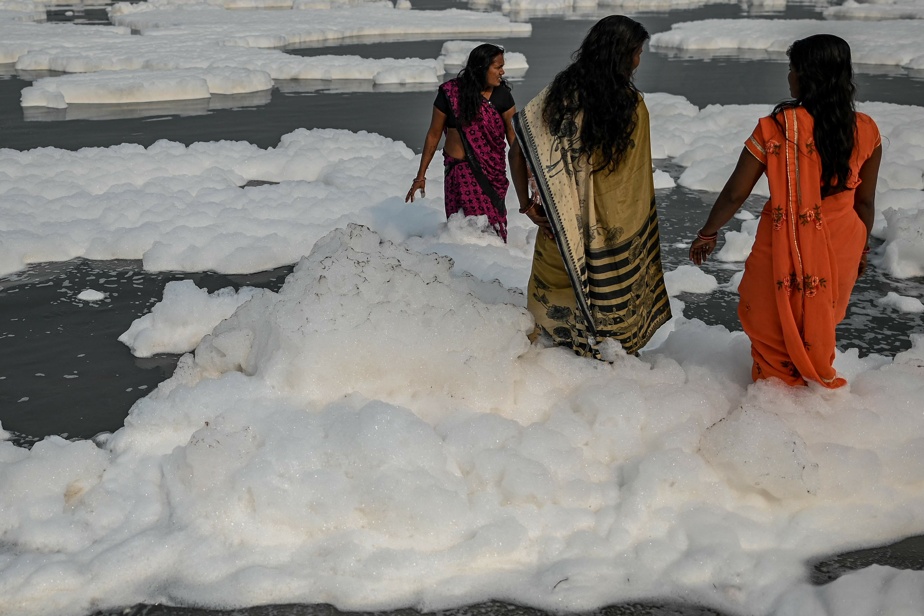
(New Delhi, India) The Yamuna, one of India’s holiest rivers, overflowed with toxic foam on Monday, further exacerbating the ailments of New Delhi residents with the dense fog of pollution already surrounding the Indian capital.
The Yamuna, a tributary of the Ganges, is already one of the most polluted rivers in the country and white foam clusters dripped on Monday as it passed through Delhi.
Local officials blamed the “significant influx of sewage and industrial waste” in the upstream last week.
Pollution did not prevent Hindu worshipers from diving into the river to celebrate the four-day Chhat Puja festival with prayers in the sun.
However, local officials said the phenomenon had disrupted water supply to some part of the city, noting how many homes had been affected.
“I thank the affected residents for their cooperation,” Raghav Chadha, vice-president of the city water supply authority, said in a statement on Sunday. “Our team of managers and engineers are working day and night to alleviate the water woes of the people of Delhi.”
Authorities have long been committed to cleaning up the Yamuna River, to no avail, and episodes of toxic foam are repeated every year.
By 2020, a government report predicts that water quality in the river will “severely” decline over the past five years.
The Indian capital and its environs have been gripped by dense toxic fog at the same time since last week.
New Delhi is one of the most polluted cities on the planet due to toxic gases emitted from industries and road traffic and air-infested farm burns every winter. They joined forces last week with illegal fireworks set off on the Hindu festival of Diwali.
Levels of PM2.5 particles – the best and most dangerous particles of air pollution – have crossed the 400 mark in many places, 16 times higher than the safety limit recommended by the World Health Organization.